Unfortunately, Manchester’s history is not only filled with achievements, discoveries, and groundbreaking revolutions but also with dark chapters involving tragic events and losses. One such devastating event occurred on August 22, 1985, at Manchester Airport when a catastrophic airplane crash claimed the lives of 55 people and left many others injured. This tragic incident forced the UK’s aviation industry to strengthen its safety measures and implement new standards to prevent similar disasters in the future. Read more on manchester-future.
About the Aircraft Involved in the Accident
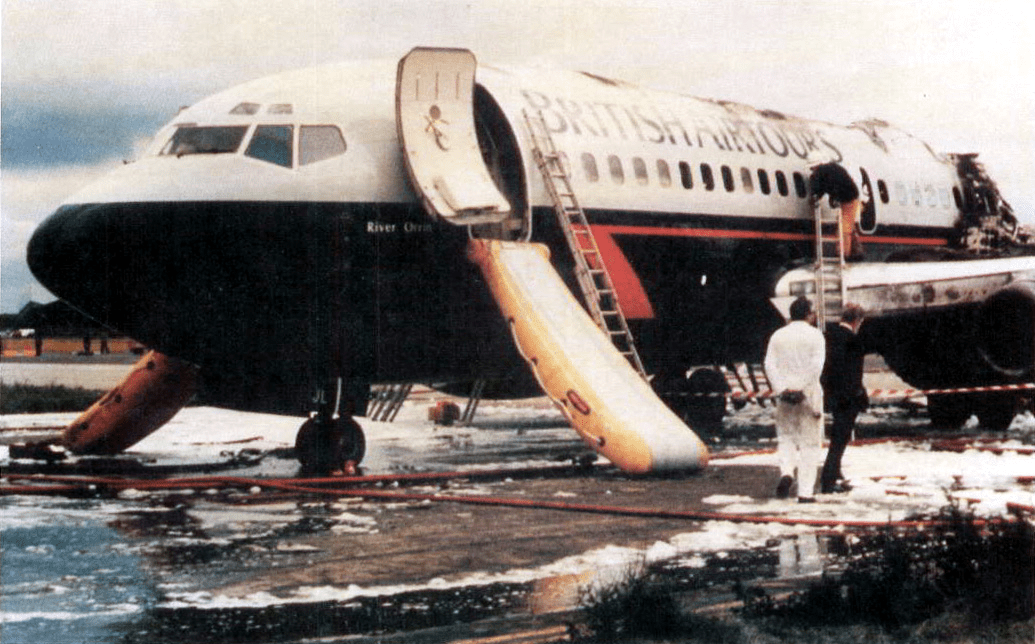
The aircraft involved in the crash was a relatively new Boeing 737-236(A), built in the 1980s. It had the registration number G-BGJL, manufacturer serial number (MSN) 22033, and line number 743. The aircraft first flew in 1981 and was equipped with PW JT8D-15 engines.
At the time of the accident, the aircraft was named “River Orrin” and operated by British Airtours, a subsidiary of British Airways.
The Crash: Everything Happened Suddenly

Flight 28M operated by British Airtours on the Boeing 737-236(A) was scheduled to fly from Manchester Airport to the Greek island of Corfu. Onboard were 131 passengers, most of whom were heading for a vacation, and six crew members.
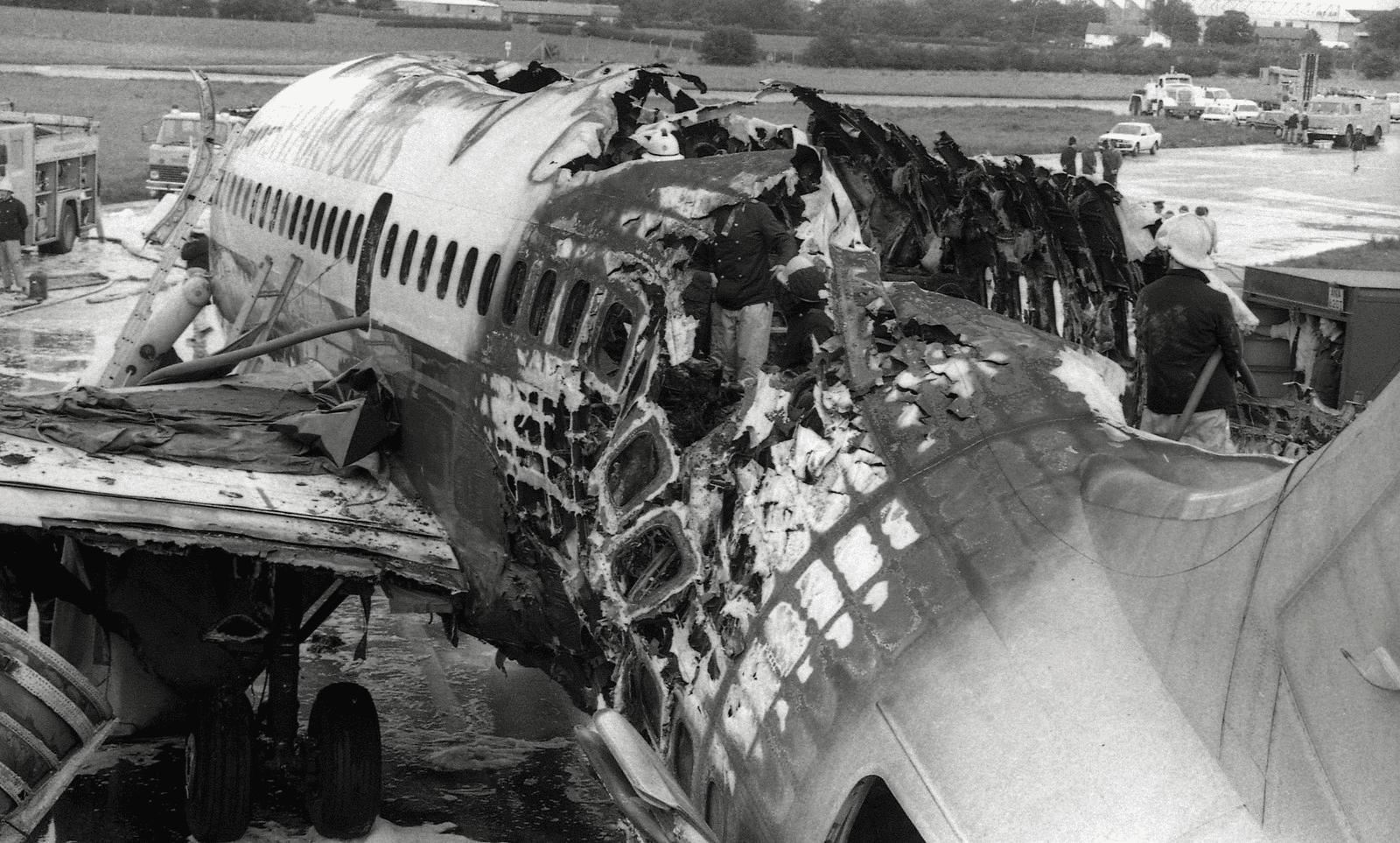
The airplane taxied to Runway 24 for takeoff at approximately 7:13 a.m. Everything seemed to be going as planned, and passengers, mostly Manchester residents, were eagerly anticipating their long-awaited beach holidays. However, just moments after takeoff, at a speed of approximately 140 mph, a loud explosion erupted from the left engine. A catastrophic engine failure caused a fire, leading to a devastating disaster.
Rescue Efforts

The crew of the Boeing 737-236(A) immediately aborted the takeoff and stopped the aircraft on the runway. The captain sent a distress signal and ordered an emergency evacuation. The flight attendants and cabin crew attempted to maintain order amidst the chaos.
However, the flames quickly spread across the aircraft due to aviation fuel, engulfing the left side. Thick, toxic smoke filled the cabin, drastically reducing visibility and making breathing almost impossible for many passengers.
The evacuation process was hindered by several factors. The rear left exit, which was closest to the flames, forced passengers to move toward the front and right side of the aircraft. Narrow and cramped aisles slowed down the evacuation, and panic broke out among the passengers.
Despite the valiant efforts of the rescue teams and crew members, many passengers could not be saved in time.
Victims and Survivors
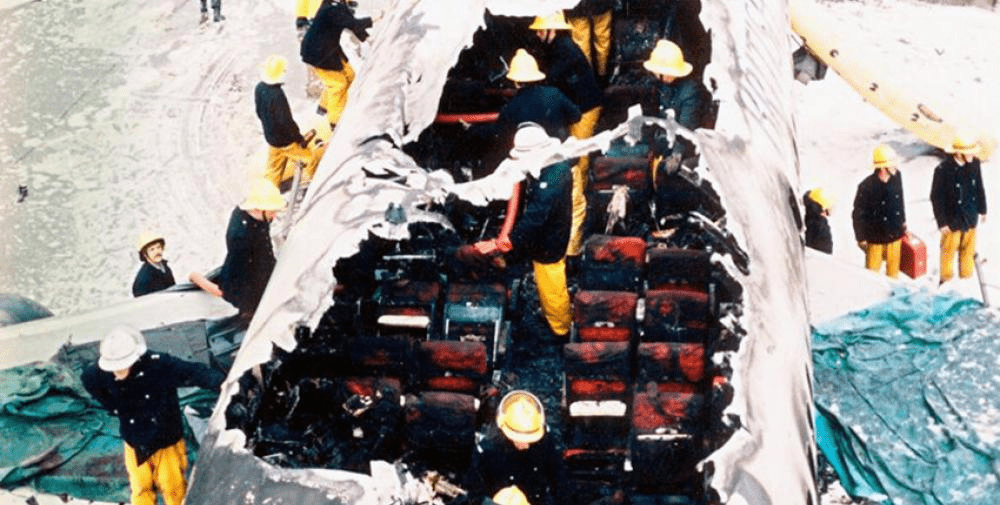

Tragically, 55 people lost their lives due to the fire and toxic smoke inhalation. Most of the victims were seated in the rear section of the aircraft, where the fire was most intense, and evacuation was exceedingly difficult. Many of those who survived suffered burns and smoke inhalation injuries. They were rushed to nearby Manchester hospitals for treatment.
Investigation and Findings
The crash was thoroughly investigated by the Air Accidents Investigation Branch (AAIB). The investigation concluded that the fire was caused by a crack in the combustion chamber of the left engine, which led to a fuel leak and subsequent ignition. The report highlighted several critical issues, including the need for improved emergency evacuation procedures and the use of fire-resistant materials in aircraft cabins.
Additionally, the toxic nature of the smoke and the failure of the forward right door significantly hampered the evacuation process and contributed to the fatalities.
The AAIB identified several factors that contributed to the tragedy:
- Vulnerability of access panels on the wing tanks to impact damage.
- Lack of effective firefighting measures for large fires within the cabin.
- Susceptibility of the aircraft’s fuselage to external flames.
- Highly toxic emissions from burning cabin materials.
Aftermath and Reforms
The tragedy that occurred in Manchester in 1985 served as a wake-up call for the aviation industry. It emphasized the urgent need to implement more effective emergency evacuation systems and fire-resistant materials in airplane interiors. Following the crash, stricter measures were introduced to enhance pre-flight inspections and improve the safety of aircraft operations.
This devastating incident remains one of the darkest moments in Manchester’s history. However, the lessons learned have since shaped safer aviation standards to prevent similar tragedies in the future.