Manchester is a unique English city, as its history dates back to Roman times. It is an incredibly rich cultural and industrial centre of Great Britain. For many years, Manchester was developing thanks to the industry. It made the city as we know it in the 21st century. Industry shaped the city’s cultural identity, architecture, economy, habits and even the population. During the 18th and 19th centuries, many people from neighbouring cities and even countries came to work in local factories and plants. Learn more at manchester-future.
The Roman era
Manchester’s early history dates back to the Roman era. The Romans were the first to establish a port on the territory of the modern city, at the confluence of the Irwell and Medlock rivers. The fort served as a strategic outpost in Roman Britain. Since then, central Manchester has been permanently inhabited. However, in the 3rd century, the Romans left the city and the settlement was abandoned until the middle of the century. Later, the Saxons settled in Manchester. Their centre shifted to the confluence of the Irwell and Irk rivers. The Saxons lived in the territory of Manchester until the mid-1060s when the Normans came to these lands.
The Middle Ages
The mediaeval era in Manchester is characterised by the development of markets and the emergence of the textile industry. During this period, Manchester gained the reputation of a trading centre of England due to its beneficial location.
Around the 14th century, Manchester faced a huge influx of immigrants. Most of them were Flemish weavers. They are considered the founders of the region’s textile industry. This industry has been developing in the city for quite a long time. At the end of the 16th century, Manchester received a reputation as a textile industrial centre.
The production of textiles, especially wool and linen, marked the beginning of a new era for Manchester. The rapid growth of the textile industry and trade laid the foundation for the prosperity and development of the city in the future, in particular, as the main industrial centre of Great Britain. Initially, the production of linen and cotton fabrics dominated in Manchester, but by the 18th century, the city focused on cotton. After all, in that era, cotton was much more important than, for example, wool. In the 18th century, there was a significant increase in cotton production. Therefore, Manchester was nicknamed Cottonopolis.
Manchester was the centre of the textile industry in England. In the 18th century, the city acquired canals for more efficient transportation of raw materials and goods. Also, in the 18th century, Manchester got a commodity exchange and many large warehouses, which contributed to the prosperity of trade and industry in the region as well.
The industrial boom
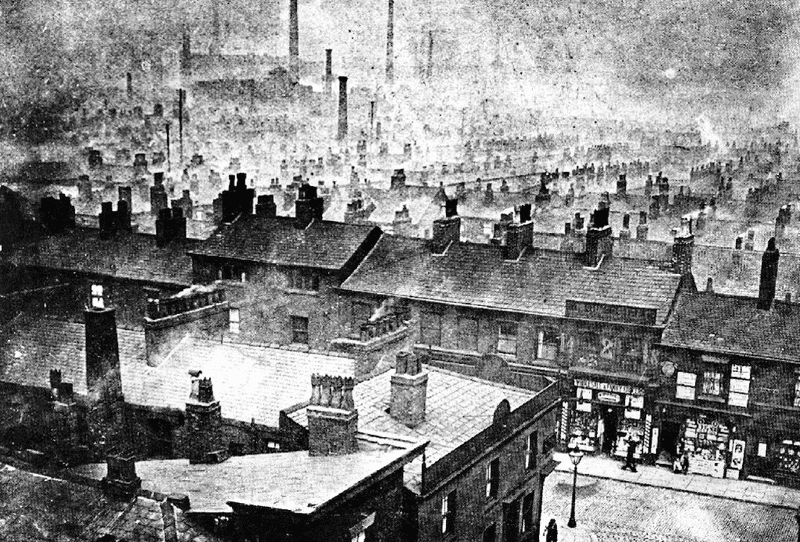

In the 19th century, Manchester experienced a period of incredible transformations. With the advent of steam power and mechanisation, the city became a centre of industrial progress. Textile factories and plants were significantly modernised, which led to an increasing demand for their products. Thanks to the introduction of innovations, Manchester’s cotton industry began to flourish at an even greater rate. In the 19th century, the city deservedly became the world leader in textile production.
The construction of the Manchester Ship Canal gave the city access to world markets. It made the import of raw materials and the export of finished products much easier. Such an industrial boom in the 19th century made Manchester one of the leaders of international trade and strengthened its status as an industrial centre.
Manchester isn’t just an industrial city
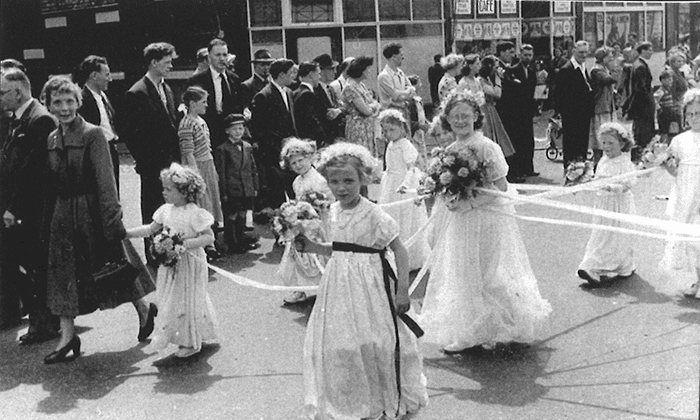

For most city residents and visitors, Manchester is associated with industry. People also know that the textile industry was shaping the city for many years. However, it isn’t the end of the list! Manchester is a very diverse city, which has its own unique artistic, architectural, theatrical and musical identity that has been formed over many centuries.
In the 20th century, Manchester became culturally influential in Great Britain. In addition to being the 5th most populous city in England, it also holds leading positions in other ratings. Thus, in addition to industry, Manchester is famous for its universities. People from different parts of the world come to study here. Therefore, Manchester remains an important industrial and cultural centre for many residents of the UK.
In addition, Manchester can boast of a unique architecture that combines a variety of styles. There are also amazing museums that take you closer to the history of the city and its industrial past. The music, theatre and sports spheres are well-developed here too.
Undoubtedly, in the 21st century, every sphere of urban life in Manchester has developed to the highest level, but its rich industrial heritage isn’t forgotten as well. People did their best to preserve it. For example, many old industrial buildings of past centuries have been restored and repurposed into museums, galleries and even into modern apartments.
The history of Manchester’s development is incredibly rich. The city has come a long way from an ancient Roman fort to a bustling and diverse metropolis in the 21st century. For many centuries, local people, trade and industry have been key components of the city’s progress.